LINK LOCAL ADDRESS
always starts w/ "fe80" followed by 3 clusters of 4 zeros
Ex. = fe80:0000:0000:0000 [last half is auto generated]
.
GLOBAL UNICAST ADDRESS aka IPv6 is automatically generated by your PC + ROUTER
Use COMMAND SCREEN: ">ipconfig" to see your IPv6 address
SUBNET MASK does not really apply to IPv6
IPv6 uses a prefix length stuck at "/64" in place of SUBNET MASK
.
.
.
.
.
.
PORT NUMBERS
*Web browser is a web client. They use WEB SERVERS (like "apache" or "i.i.s.")
DNS = Domain name system: like a speed-dialer that zips you to a site's WEB SERVER
After IP address & DNS - a PORT NUMBER gets you to the right application
.
PORT# example: 0-65535
.
*when browsing internet there are 2 port #s*
The "SOURCE" port + "DESTINATION" PORT numbers (like a train)
Webpage DATA < PORT 1 (source) < PORT 2 # (destination) < outgoing IP < intercepting IP
.Like the post office, web server just flips the destination/source - then sends back
(So different webpage tabs don't open the wrong info from multiple web-servers)
.
*FYI you can see all web-server data going back & forth between ports via RESOURCE MONITOR*
..
.
.
.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF "PORTS"
1) 0-1023 "Well Known Ports"
2) 1024-49151 "registered ports"
3) 49152-65535 "dynamic ephemeral ports"
.
.
.
**PORTS on the COMPTIA EXAM**
21-FTP
22-SSH
23-TELNET
25-SMTP
53-DNS
80-HTTP
110-POP3
161/162-SNMP
143-IMAP
443-HTTPS
4489-RDP
137-139-NETBIOS/NETBT
445-SMB.CIFS
427-SLP
548-AFP
67/68-DHCP
389-LDAP
.
.
.
.
.
.
TCP/IP, UDP, ICMP:
TCP/IP = TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL / INTERNET PROTOCOL
Connection based protocol. 2 servers talking to each other *digital handshake
.
UDP = connectionless protocol. Automated service at ice cream shop
.
ICMP = single packets of info. small Working class commands of the internet
.
.
.
PDU = protocol data unit
What part are we interested in? The frame = IP packet
tiny parts of data frame chain: "TCP segment / UDP datagram"
*3 different PDUs*
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
UNDERSTANDING DNS
DNS is like a contact list / speed dialer for the IP addresses of specific websites
DNS replaced "Host file"
ROOT SERVERS: only control one qualified domain
they're 1ST LEVEL DOMAINS like .com, edu, org, etc.
2nd level is DNS - ex: google
ROOT SERVERS top of the family tree
.com .edu .gov
\/
then DNS 2nd level domains
\/
then bottom level = my computer LOL
(When browser says "waiting for server" its going through the above family tree. Caching will save websites you've previously visited).
.
.
.
DNS server /FQDNS are limited to 256 characters (So be careful)
But 98% of the time DNS works just fine
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
WORKING with DNS
Your DHCP server usually provides the DNS
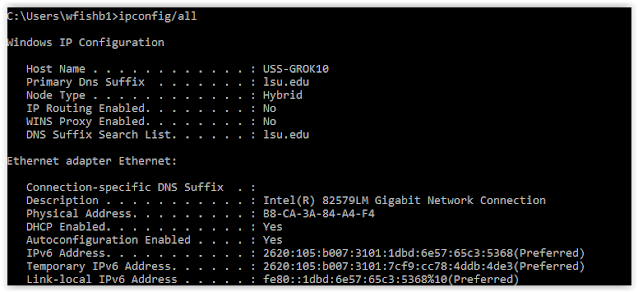
Open COMMAND SCREEN to see your DNS server - ipconfig /all
.
.
.
.
HOW TO STATICALLY CONFIGURE DNS SERVER:
CONTROL PANEL, NETWORK SHARING, CHANGE ADAPTOR SETTINGS, right click PROPERTIES, IPv properties, keep IP address automatic but manually enter 2 DNS server addresses
..
.
Alternate DNS is just a bunch of 8s?? or 8.8.4.4
"nslookup" tool: will let you see if a DNS server is working. If DNS times out, you'll know it's down.
Open COMMAND SCREEN - "nslookup"














Comments
Post a Comment